Conditional Statements in Python
Learn if-else statements with an example to check if a number is even or odd.
Conditional Statements in Python
You know how sometimes your code needs to make choices? Like "do this if something's true, otherwise do that"? That's exactly what conditional statements are for.
Python's if-else is super straightforward. It basically asks a yes/no question and runs different code based on the answer.
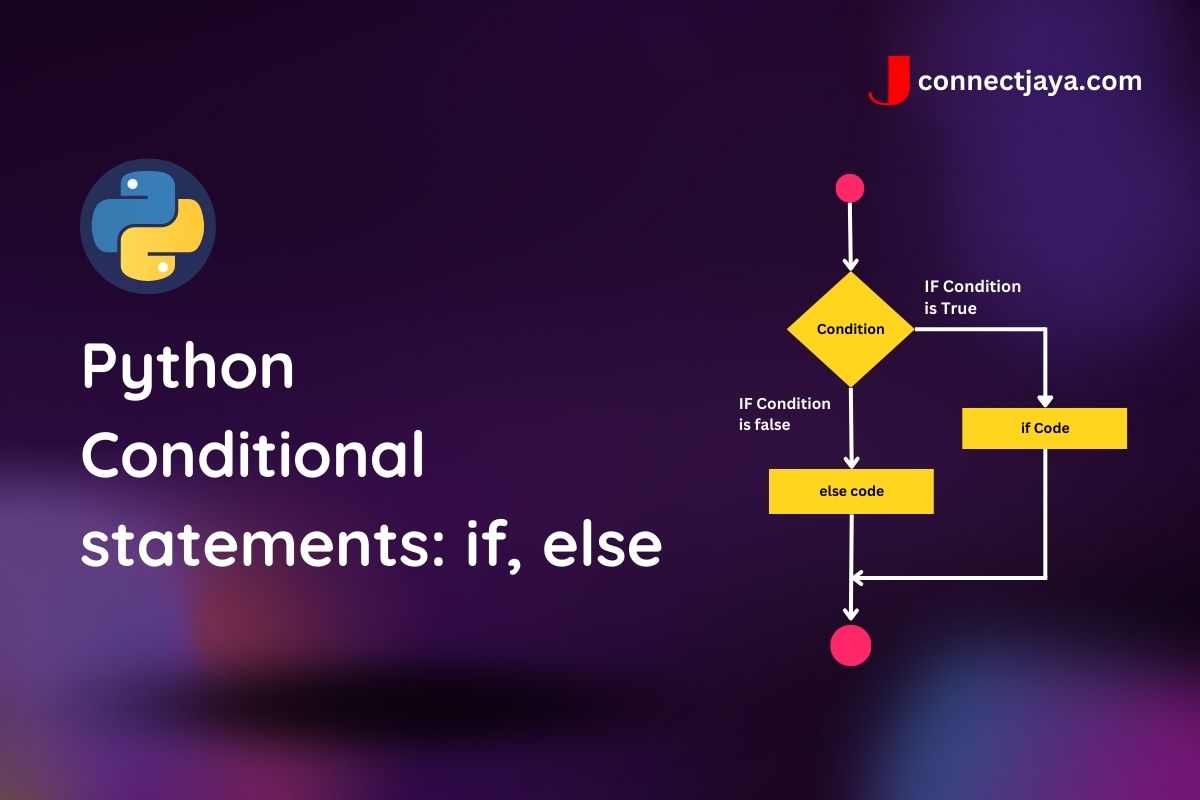
The Basic Idea
Think of it like this: you check if something is true or false, then tell Python what to do in each case.
Here's what it looks like:
if condition:
# runs when condition is true
else:
# runs when condition is false
Example: Is This Number Even or Odd?
Here's a quick program that figures out if a number is even or odd.
# Program to check if a number is even or odd
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number % 2 == 0:
print("The number is even.")
else:
print("The number is odd.")
What's Happening Here?
- You type in a number
- Python divides it by 2 and checks the remainder (
number % 2 == 0) - No remainder? It's even
- Got a remainder? It's odd
Things You Can Try
Want to experiment? Here are some ideas:
- Test it with negative numbers and see what happens
- Put it in a
whileloop so you can check multiple numbers without restarting - Add another check to see if the number is positive or negative
Wrapping Up
Honestly, once you get comfortable with if-else statements, you can build way more interesting stuff. They show up everywhere — login systems, game logic, you name it.
The cool thing about Python is it reads almost like English, so these decisions feel pretty natural to write.